Year-Round Tax-Saving Strategies to Lower Your 1040 Taxes
Saving money on taxes isn’t just for tax season—it requires year-round planning. Here are proactive strategies to help you lower your 1040 tax bill and maximize deductions throughout the year.
1. Adjust Your Tax Withholding Early in the Year
✅ If you received a large tax refund, you’re overpaying taxes throughout the year.
✅ If you owed taxes, you may need to increase withholdings or make estimated payments.
✅ Use IRS Form W-4 to adjust your withholdings at work.
🔗 Related: Understanding Your 1040 Tax Return
2. Max Out Retirement Contributions
✅ 401(k) contributions reduce taxable income—limit for 2024 is $23,000 ($30,500 if 50+).
✅ Traditional IRA contributions are tax-deductible—limit is $7,000 ($8,000 if 50+).
✅ Self-employed? Consider a Solo 401(k) or SEP IRA.
🔗 Related: How 2025 Contributions to IRA & 401(k) Can Reduce 2024 Taxes
3. Take Advantage of Tax Credits
✅ Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) – Available to low-to-moderate income taxpayers.
✅ Child Tax Credit (CTC) – Up to $2,000 per child.
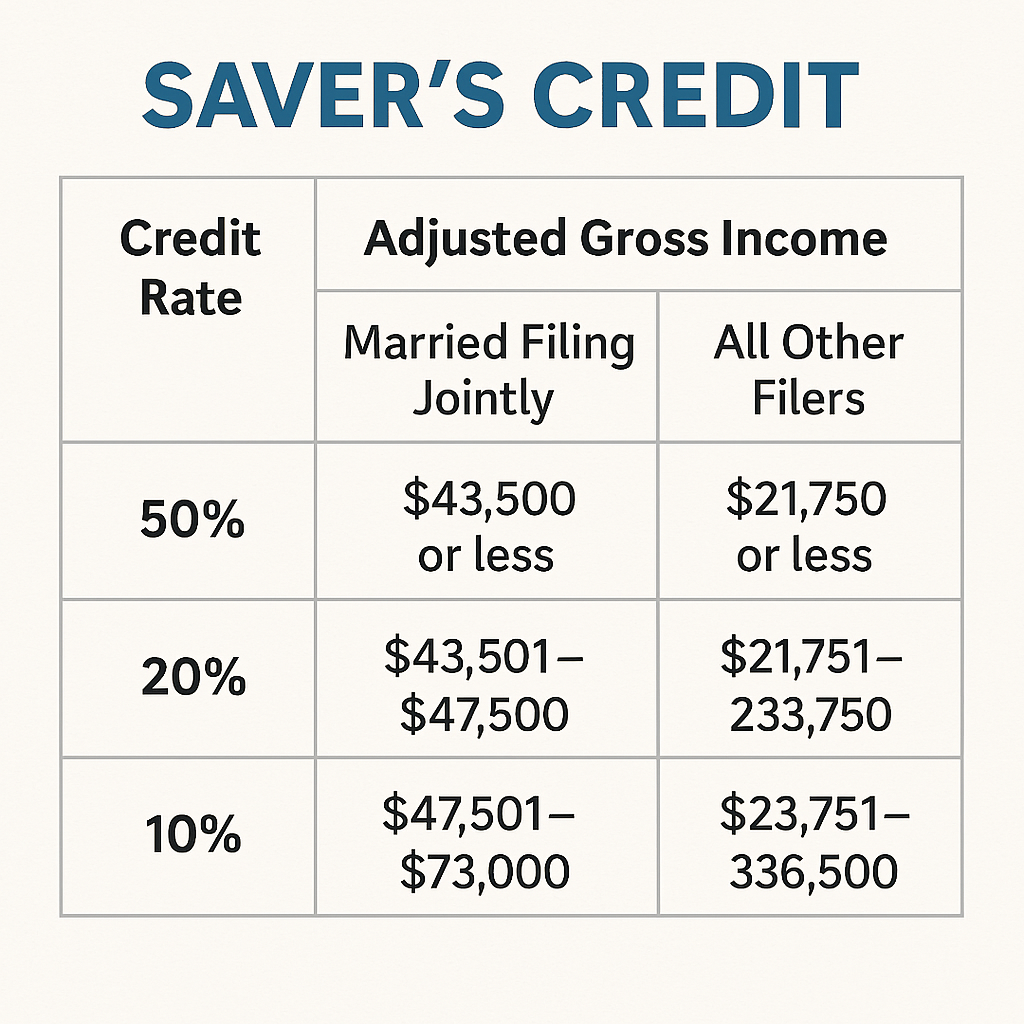
✅ Saver’s Credit – For contributing to retirement accounts.
🔗 Related: Your Guide to Tax Credits & Deductions
4. Track and Deduct Work-Related Expenses
✅ Self-employed? Deduct business expenses like home office, internet, and vehicle costs.
✅ Employees working remotely? Check if you qualify for home office deductions.
✅ Freelancers and side hustlers should keep receipts and mileage logs.
🔗 Related: How Small Business Owners Can Reduce Their Tax Burden
5. Contribute to a Health Savings Account (HSA) or Flexible Spending Account (FSA)
✅ HSA contributions are tax-deductible, grow tax-free, and withdrawals for medical expenses are tax-free.
✅ FSA funds are pre-tax but must be used within the year.
🔗 Related: The Health Savings Account (HSA): A Triple Tax Advantage
6. Harvest Capital Losses to Offset Gains
✅ Sell underperforming stocks to offset capital gains taxes.
✅ Can offset up to $3,000 in ordinary income per year.
🔗 Related: IRS Tax Law Changes for 2025
Final Thoughts
Lowering your tax bill requires planning all year long. Take advantage of deductions, credits, and tax-saving investments to keep more of your money.
🚀 Next Steps:
- Adjust your tax withholding today.
- Contribute to retirement and HSA accounts.
- Keep organized records of expenses and deductions.
🔗 Need more tax guidance? Visit our Tax-Saving Blog & Expert Insights.